Create React App의 serviceWorker는 무엇일까
개요
// This optional code is used to register a service worker.
// register() is not called by default.
// This lets the app load faster on subsequent visits in production, and gives
// it offline capabilities. However, it also means that developers (and users)
// will only see deployed updates on subsequent visits to a page, after all the
// existing tabs open on the page have been closed, since previously cached
// resources are updated in the background.
// To learn more about the benefits of this model and instructions on how to
// opt-in, read https://bit.ly/CRA-PWA
const isLocalhost = Boolean(
window.location.hostname === 'localhost' ||
// [::1] is the IPv6 localhost address.
window.location.hostname === '[::1]' ||
// 127.0.0.0/8 are considered localhost for IPv4.
window.location.hostname.match(
/^127(?:\.(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)){3}$/,
),
)
type Config = {
onSuccess?: (registration: ServiceWorkerRegistration) => void
onUpdate?: (registration: ServiceWorkerRegistration) => void
}
export function register(config?: Config) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' && 'serviceWorker' in navigator) {
// The URL constructor is available in all browsers that support SW.
const publicUrl = new URL(process.env.PUBLIC_URL, window.location.href)
if (publicUrl.origin !== window.location.origin) {
// Our service worker won't work if PUBLIC_URL is on a different origin
// from what our page is served on. This might happen if a CDN is used to
// serve assets; see https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app/issues/2374
return
}
window.addEventListener('load', () => {
const swUrl = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/service-worker.js`
if (isLocalhost) {
// This is running on localhost. Let's check if a service worker still exists or not.
checkValidServiceWorker(swUrl, config)
// Add some additional logging to localhost, pointing developers to the
// service worker/PWA documentation.
navigator.serviceWorker.ready.then(() => {
console.log(
'This web app is being served cache-first by a service ' +
'worker. To learn more, visit https://bit.ly/CRA-PWA',
)
})
} else {
// Is not localhost. Just register service worker
registerValidSW(swUrl, config)
}
})
}
}
function registerValidSW(swUrl: string, config?: Config) {
navigator.serviceWorker
.register(swUrl)
.then((registration) => {
registration.onupdatefound = () => {
const installingWorker = registration.installing
if (installingWorker == null) {
return
}
installingWorker.onstatechange = () => {
if (installingWorker.state === 'installed') {
if (navigator.serviceWorker.controller) {
// At this point, the updated precached content has been fetched,
// but the previous service worker will still serve the older
// content until all client tabs are closed.
console.log(
'New content is available and will be used when all ' +
'tabs for this page are closed. See https://bit.ly/CRA-PWA.',
)
// Execute callback
if (config && config.onUpdate) {
config.onUpdate(registration)
}
} else {
// At this point, everything has been precached.
// It's the perfect time to display a
// "Content is cached for offline use." message.
console.log('Content is cached for offline use.')
// Execute callback
if (config && config.onSuccess) {
config.onSuccess(registration)
}
}
}
}
}
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error('Error during service worker registration:', error)
})
}
function checkValidServiceWorker(swUrl: string, config?: Config) {
// Check if the service worker can be found. If it can't reload the page.
fetch(swUrl, {
headers: { 'Service-Worker': 'script' },
})
.then((response) => {
// Ensure service worker exists, and that we really are getting a JS file.
const contentType = response.headers.get('content-type')
if (
response.status === 404 ||
(contentType != null && contentType.indexOf('javascript') === -1)
) {
// No service worker found. Probably a different app. Reload the page.
navigator.serviceWorker.ready.then((registration) => {
registration.unregister().then(() => {
window.location.reload()
})
})
} else {
// Service worker found. Proceed as normal.
registerValidSW(swUrl, config)
}
})
.catch(() => {
console.log(
'No internet connection found. App is running in offline mode.',
)
})
}
export function unregister() {
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
navigator.serviceWorker.ready
.then((registration) => {
registration.unregister()
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error.message)
})
}
}
서비스 워커란 브라우저에서 실행되는 스크립트 파일이다. 이 파일에서 직접적으로 DOM을 다뤄서는 안된다. 여기에는 별도 구성 없이 사용하라 수 있는 네트워크 관련 기능들이 존재한다. 서비스 워커는 오프라인 경험을 제공하기 위해서 존재한다. 여기에는 푸쉬 알림, 백그라운드 동기화 등이 있다.
리액트에서 서비스 워커를 적절하게 구성할 수 있다면, 네트워크 요청을 가로채서 관리함으로써 다양한 작업등을 할 수 있다. create-react-app을 사용하면 서비스 워커는 SWPrecacheWebpackPlugin를 통해 자동으로 설치된다. 서비스 워커는 네트워크가 새로운 요청을 처리하기 위한 병목현상이 되지않도록 한다.
서비스워커: 유즈케이스
이는 개발자가 심리스한 연결성을 보여주기 위해서는, 가장 먼저 해결해야 할 문제가 바로 네트워크 연결 중단이다. 최근에는 좋은 사용자 경험을 제공하는 오프라인 어플리케이션의 개념이 인기를 끓고 있다. 서비스워커는 웹 개발자에게 다음과 같은 이점을 제공한다.
- 웹사이트의 성능향상. 웹사이트의 로딩 속도를 빠르게 하기 위해 사이트 일부를 캐싱할 수 있다.
- 오프라인 화면을 제공하여, 연결이 끊기더라도 정상적으로 애플리케이션을 계속 사용하도록 할 수 있다.
- 기존 웹 기술로는 불가능한 알림과 푸쉬 API를 활용할 수 있다.
- 백그라운드 동기화를 수행할 수 있게 해준다. 사용자에게 원활한 환경을 제공하기 위해, 네트워크 연결이 다시 복원될 때 까지 특정 작업을 연기할 수 있다.
서비스워커의 라이브사이클
서비스워커의 라이프 사이클은 웹 애플리케이션과 관련이 없다. 자바스크립트를 활용하여 서비스 워커를 등록하면 설치가 된다. 이는 브라우저가 백그라운드에서 설치를 시작하도록 지시한다. 또한 필요한 에셋을 이 기간 동안 캐시할 수도 있다. 설치가 끝나면 활성화 프로세스가 시작된다. 활성화되면, 서비스 워커는 해당 범위의 모든 페이지와 연결되며, 이벤트에 의해 호출되지 않는 한 프로세스가 종료된다.
서비스워커의 라이프 사이클은 일반적으로 개발자가 코딩해야 한다. 리액트의 서비스 워커의 경우, 리액트 자체로 라이프 사이클을 관리하여 개발자가 조금더 서비스 워커를 다루기 쉽게 했다.
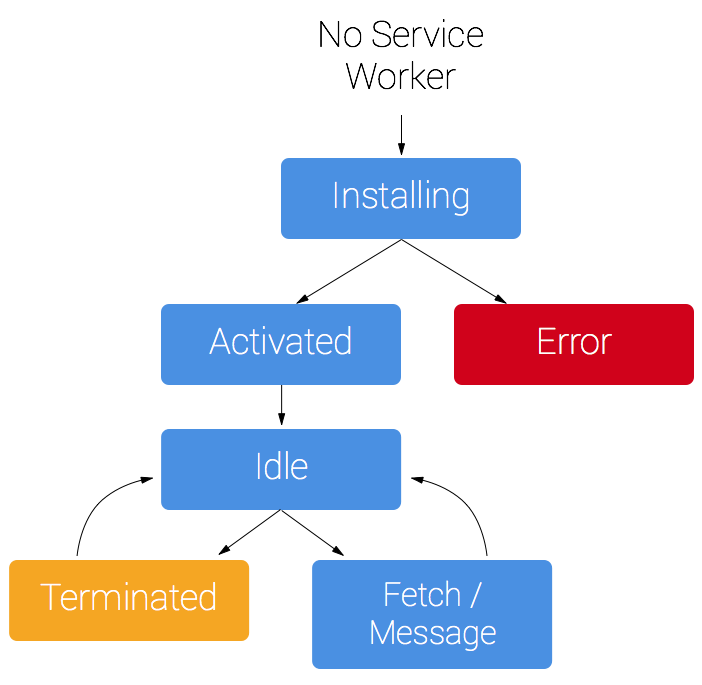
리액트 서비스 워커의 고려사항
- 서비스 워커는 브라우저에 의해 자체 글로벌 스크립트 컨텍스트에서 실행된다. 이는 즉, 페이지의 DOM 요소에 접근해서는 안된다는 것을 의미한다. 따라서, 페이지와의 통신이 필요하다면 간접적인 방식으로 처리해야 한다. 보통 postMessage를 사용한다.
- 서비스 워커는 HTTPS 프로토콜에서만 실행된다.
localhost는 제외. - 서비스 워커는 특정 페이지에 종속되어 있지 않으므로, 재사용이 가능하다.
- 서비스워커는 이벤트 중심으로 이루어져 있다 (event driven). 이는 서비스 워커가 종료되면 어떠한 정보도 얻을 수 없다는 것을 의미한다. 이전 상태의 정보에 접근하기 위해서는, IndexedDB API를 사용해야 한다.
리액트 서비스워커 활성화
create-react-app으로 리액트 어플리케이션을 만들면, 아래와 같은 구조를 띄고 있을 것이다.
├── README.md
├── node_modules
├── package.json
├── .gitignore
├── build
├── public
│ ├── favicon.ico
│ ├── index.html
│ └── manifest.json
└── src
├── App.css
├── App.js
├── App.test.js
├── index.css
├── index.js
├── logo.svg
└── serviceWorker.js
```
serviceWorker.js가 src 밑에 존재한다. 이 파일은 디폴트로 생성된다. 이 단계에서는 서비스워커는 등록되지 않았으므로, 서비스 워커를 사용하기 위해서는 이를 등록해야 한다.
src/index.js의
serviceWorker.unregister()
를
serviceWorker.register()
로 바꾼다. 이렇게 딱 한줄만 바꾸면, 리액트 애플리케이션의 서비스 워커를 사용할 준비가 된다.
일반적인 웹 애플리케이션에서는, 서비스워커의 전체 라이프 사이클을 코딩해야 한다. 그러나 리액트는 기본값으로 이러한 개발을 할 준비를 해두었다. src/serviceWorker.js 파일을 확인해보면, 서비스워커와 관련된 코드가 준비되어 있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
개발환경에서 리액트 서비스 워커 작업하기
serviceWorker.js의 register() 함수를 보면, process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' 때문에 프로덕션 모드에서만 실행된다는 것을 알 수 있다. 이를 수정할 방법이 몇가지 있다.
- 이조건을 삭제하여 development에서도 실행하는 방법. 그러나 잠재적인 이슈가 있을 수 있다.
- 리액트 애플리케이션을 프로덕션 버전으로 만들어서, 서빙하는 방법. 아래와 같은 방법으로 사용하면 된다.
$ yarn global add serve
$ yarn build
$ serve -s build
서비스 워커를 커스터마이징 하는법
CRA에서 service-worker.js는 기본적으로 모든 기본 에셋을 캐싱한다. 서비스 워커에 기능을 추가하기 위해서는, custom-service-worker.js를 만들고, register()를 수정해서 커스터마이징 하는 방법이 있다.
34번째 라인에 가서, 아래와 같이 수정하면 된다.
window.addEventListener('load', () => {
const swUrl = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/custom-service-worker.js`;
//
}
package.json을 아래와 같이 수정한다.
"scripts": {
"start": "react-app-rewired start",
"build": "react-app-rewired build",
"test": "react-app-rewired test",
"eject": "react-app-rewired eject"
},
그리고, Google의 workbox plugin을 추가한다. Google's Workbox plugin
npm install --save-dev workbox-build
다음에, CRA에 커스텀 서비스 워커를 삽입하도록 지시하는 설정파일을 생성한다.
const WorkboxWebpackPlugin = require('workbox-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = function override(config, env) {
config.plugins = config.plugins.map((plugin) => {
if (plugin.constructor.name === 'GenerateSW') {
return new WorkboxWebpackPlugin.InjectManifest({
swSrc: './src/custom-service-worker.js',
swDest: 'service-worker.js',
})
}
ㄴ
return plugin
})
return config
}
다음 아래와 같이 특정 디렉토리를 캐시하는 커스텀 서비스 워커를 만들 수 있다.
workbox.routing.registerRoute(
new RegExp('/path/to/cache/directory/'),
workbox.strategies.NetworkFirst(),
)
workbox.precaching.precacheAndRoute(self.__precacheManifest || [])
변경사항을 적용하기 위해서는 애플리케이션을 다시 빌드하면 된다.
더 공부해보기
https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/primers/service-workers/
서비스 워커는 브라우저가 백그라운드에서 실행하는 스크립트로, 웹페이지와는 별개로 작동하며, 웹페이지 또는 사용자 상호작용이 필요하지 않은 기능에 대해 문호를 개방합니다. 현재 푸시 알림 및 백그라운드 동기화와 같은 기능은 이미 제공되고 있습니다. 향후 서비스 워커는 주기적 동기화 또는 지오펜싱과 같은 다른 기능을 지원할 수 있습니다. 이 가이드에서는 프로그래밍 방식의 응답 캐시 관리를 비롯하여 네트워크 요청을 가로채고 처리하는 핵심 기능에 대해 설명합니다.
https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app/pull/1728
https://developers.google.com/web/tools/workbox/modules/workbox-webpack-plugin#generatesw_plugin